Signs of different headaches need to be known as an individual can deal better with a headache. By knowing more about health tips for headaches, a person can keep better health.
Stress and modern lifestyles cause headaches. Knowing more about the health tips of different headaches helps.
Table of Contents
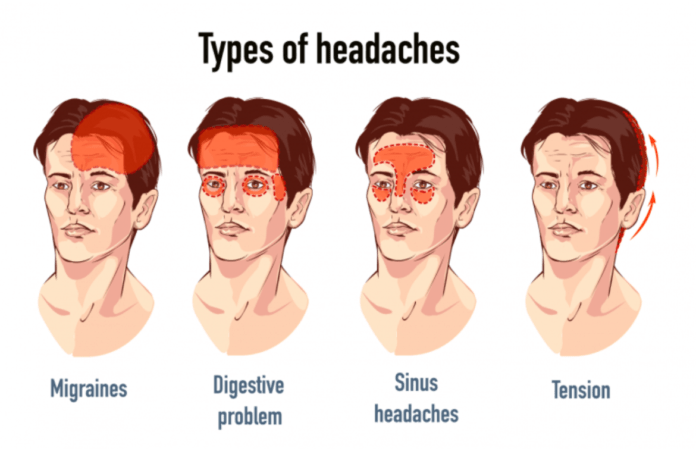
Tension headache
If having a tension headache, a person feels a dull, aching sensation all over one’s head. It is not throbbing.
Symptoms:
Tenderness or perhaps sensitivity around one’s neck, forehead, scalp, or shoulder muscles also might occur.
Cluster headache
Cluster headaches show signs of severe burning as well as piercing pain and occur around or behind the eye or on one side of the face at a time.

Symptoms:
- Swelling, redness, flushing, as well as sweating on the side that’s affected by the headache
- Nasal congestion as well as eye tearing on the same side as the headache
Migraine
Migraine pain happens to be an intense pulsing from deep within one’s head. This pain lasts for days and affects one’s daily routine.
Symptoms
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- flashing lights
- shimmering lights
- zigzag lines
- stars
- shimmering lights
- blind spots
POSSIBLE MEDICAL EMERGENCY
The symptoms of a stroke can also appear as a migraine headache. It is better to seek immediate medical attention.
Common migraine triggers are:
- Skipped meals
- Dehydration
- Some foods
- Hormone fluctuations
- Exposure to chemicals
Hemicrania continua
Hemicrania continua as a moderate headache occur on one side of one’s head lasting continuously for at least 3 months. It is very common in women.
This headache is accompanied by:
- Tearing or eye redness
- Nasal congestion or runny nose
- Eyelid drooping
- Forehead sweating
- Miosis
- Restlessness or agitation
Ice pick headache
Thunderclap headache
A thunderclap headache can be an extremely severe headache that does come on rapidly, reaching peak intensity in under a minute. It may be benign, but it can also be a symptom of a serious condition, requiring immediate medical attention.
In a few cases, a thunderclap headache means:
- Blood vessel tears, ruptures, or blockages
- Brain injury
- Stroke
- Reversible cerebral vasoconstriction syndrome (RCVS)
- Vasculitis (inflammation of blood vessels)
- Pituitary apoplexy (bleeding into or loss of blood from an organ)
The most common secondary headaches occurring due to other ailments are:
Allergy or sinus headache
Headaches occur as a result of an allergic reaction and they appear in one’s sinus area and the forehead.
Hormone headache
Women commonly experience headaches due to hormonal fluctuations. Menstruation, and making use of birth control pills, as well as pregnancy can affect estrogen levels, which can cause a headache. This is known as menstrual migraine.
Caffeine headache
Caffeine affects blood flow to one’s brain. Having too much can lead to headaches, such as quitting caffeine. People who have frequent migraine headaches are at risk of having a headache due to caffeine use.
Exertion headache
Exertion headaches occur quickly after periods of intense physical activity. Weightlifting, running, as well as sexual intercourse are all common triggers of an exertion headache. An exertion headache should not last too long.
Hypertension headache
High blood pressure causes a headache. This does require an emergency at times. The effect of pain is on both sides of one’s head and gets worse with activity. It often has a pulsating quality.
MEDICAL EMERGENCY
If experiencing a hypertension headache, seek immediate medical attention if faced with:
- Changes in vision
- Nosebleeds
- Numbness or tingling
- Chest pain
- Shortness of breath
This headache develops if treated for high blood pressure.
Rebound headache
Rebound headaches, due to medication overuse headaches, are dull, tension-type headaches, or intensely painful, like a migraine headache. Frequently, using over-the-counter (OTC) pain relievers causes this headache.
Post-traumatic headache
Post-traumatic headaches develop after any type of head injury. These do last up to 6 to 12 months after the injury. They can become rather chronic.
Spinal headache
A spinal headache is due to low cerebrospinal fluid pressure following a lumbar puncture.
symptoms of spinal headache include:
- Nausea
- Neck pain
- Dizziness
- Tinnitus
- Visual changes
- Hearing loss
- Radiating pain in the arms.