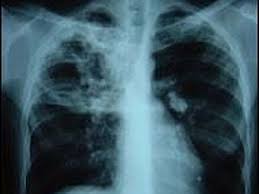
Tuberculosis (TB)-Lung disease Tuberculosis is one of the most widespread infectious diseases caused due to bacterial infection. It is widely spread in developing countries due to poor immune system and less hygienic conditions. The bacterial genus which causes tuberculosis is Mycobacterium. Among many strains of bacterium the most virulent and causative infection of TB is genus tuberculosis. It affects mainly lungs called as pulmonary tuberculosis and it can also affect other body parts termed as extra pulmonary tuberculosis, although extra pulmonary TB occurs along with pulmonary tuberculosis.
What is Tuberculosis (TB)-Lung disease
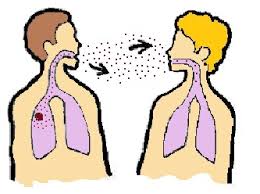
TB spreads through contaminated air, when an infected person coughs or sneezes it is spread. It can be transmitted through respiratory fluids too. Even though a healthy person gets in contact with the tuberculosis bacterium he may not show symptoms since TB can be latent in the cell, this is called as latent tuberculosis. During latent period of tuberculosis the person cannot spread the disease to another person. It may not become active immediately
but later on it may become active.
Tuberculosis (TB)-Lung disease Symptoms
- In active tuberculosis infection the following are the symptoms
- Chronic cough with blood sputum
- Pain in chest
- Shortness of breath
- Fever and night sweats, chills
- Loss of appetite and Weight loss
- Fatigue
- Nail clubbing
Tuberculosis (TB)-Lung disease Diagnosis
Active TB can be detected through radiology commonly x-rays on chest and as well as microscopic examination of the body fluids and microbiological culturing of the body fluids of an infected person.
Latent TB diagnosis is relied on tuberculin skin test and blood test.
Tuberculosis (TB)-Lung disease Treatment
Treatment of active TB is difficult and requires administration of many antibiotics over long period of time until the infection is subsided. It will last up to 6 months or longer. combination of antibiotics containing rifampicin, isoniazid, pyrazinamide, and ethambutol for the first two months, and only rifampicin and isoniazid for the last four months are used, If antibiotics are discontinued or with irregular using infection prevails and it will further create problems by becoming multi drug resistant. Due to this use of many different antibiotics the bacterium started to gain antibiotic resistant to wide range of commonly used drugs this resulted in evolving of multi drug resistant bacteria.
You may need to stay at home or be admitted to a hospital for 2 to 4 weeks to avoid spreading the disease to others until you are no longer contagious.
If left untreated there are severe complications. The following are the complications:
- Back pain and stiffness of the spine

- TB arthritis affects the hips and knees
- The membranes around the brain meningitis swell due to this persistent headaches and mental changes may also take place
- The functions of heart kidney and lever may impair.
Vaccination & prevention
- Proper screening of TB affected individual and proper care should be take care for isolating the affected individual in order to stop further spreading of the disease.
- Vaccination is done by injecting Bacillus Calmette Guerin (BCG) vaccine
- Pulmonary TB can cause permanent lung damage if not treated early.
- There may be side effects caused due to the treatment which involves usage of many drugs. Changes in vision, development of rash, change in urine coloration are few side effects.
The above are the details of Tuberculosis (TB)-Lung disease